使用哈希查找算法分为两步:
- 用散列函数将被查找的键(key)转换为哈希表的一个索引。理想情况下,不同的键都能转换成不同的索引值。实际上我们需要面对两个或多个键都会散列到相同的索引值的情况。
- 处理碰撞冲突的过程。常见的两种方式:拉链法和线性探测法。
哈希函数
一般拥有如下特征:
- 相同的输入经哈希计算后得出相同输出。
- 不同的输入经哈希计算后一般得出不同输出值,但也可能会出现相同输出值。
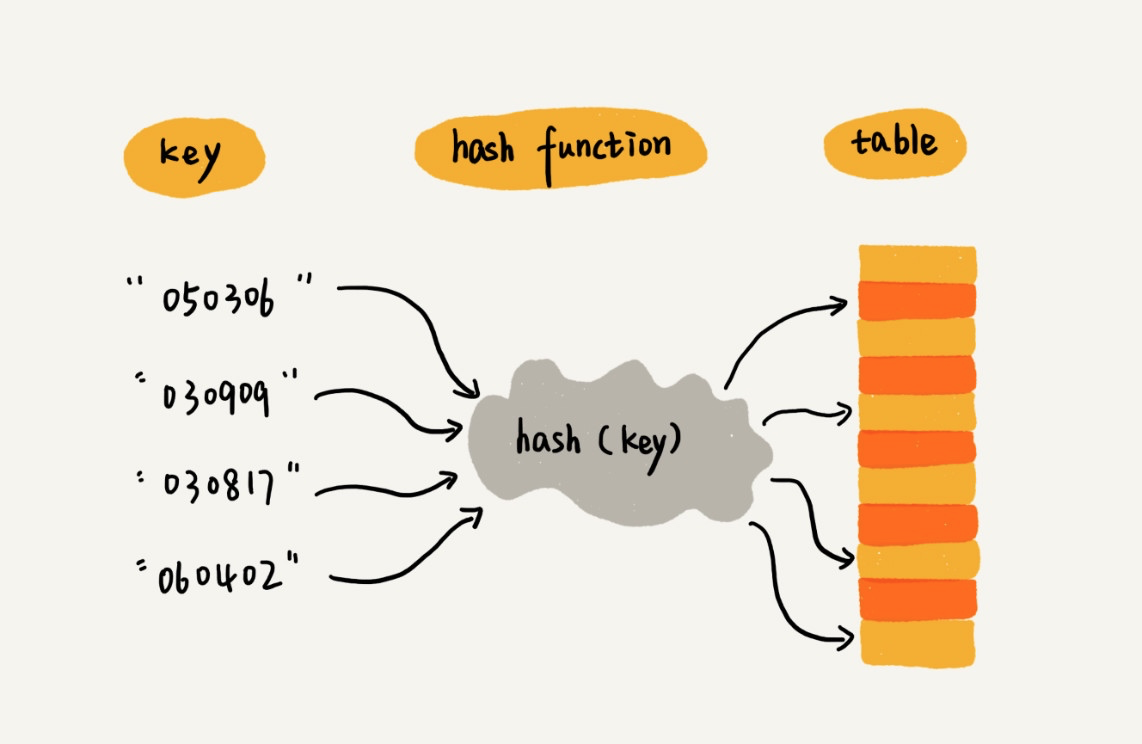 28971f3cacf598bcfa5fa6f85dc0cdb9.png
28971f3cacf598bcfa5fa6f85dc0cdb9.png
我们要找的散列函数应该易于计算并且能够均匀分布所有的键。
哈希冲突以及解决方案
线性探测
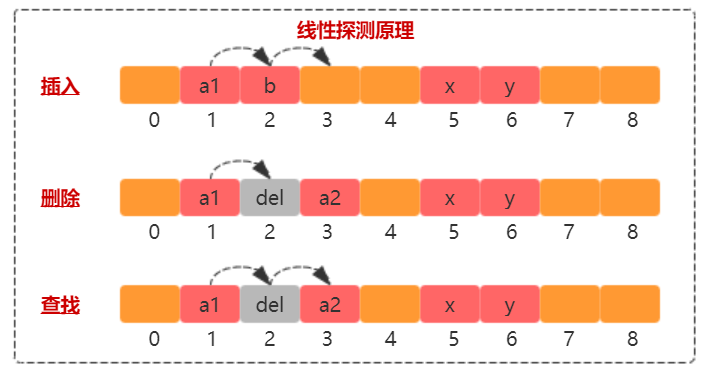 a1320d1df331a04be04a9c2526988a02.png
a1320d1df331a04be04a9c2526988a02.png
插入:插入元素 a2,哈希计算得到的索引发现和 a1
存在冲突(即已经被占用),往后寻找,发现下一个位置被 b
占用,继续往下寻找到 arr[3] 有空位,存储 a2。
删除:删除元素 a2,哈希计算得到索引,
发现并不是要删除的元素,继续往下找,找到 arr[3] 并标记为
del。之所以不实际删除,是数组只能从后往前覆盖,这就打乱整个哈希表的记录了,故标记为
del 即可。
查找:查找元素 a2,哈希计算得到索引,
发现并不是要查找的元素,继续往下找,找到 arr[3],返回查询结果。
拉链法
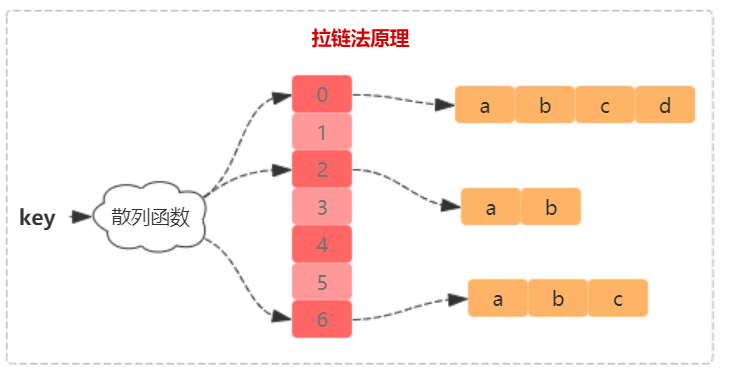 b8826396f5f5e0d16814a152d5ac8e4a.png
b8826396f5f5e0d16814a152d5ac8e4a.png
插入不同元素相同哈希的结果,通过单链表串联起来。对于删除和查找很容易理解,不多赘述。
Redis 字典的实现
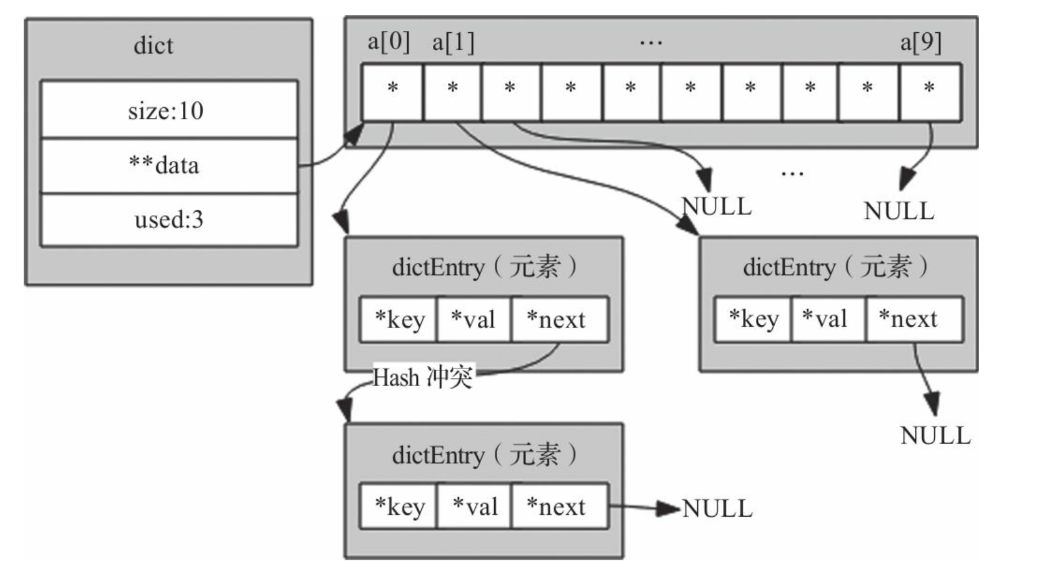 image20250131152347650.png
image20250131152347650.png
结构体
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next;
};
|
dictEntry 成员 v
的设计是一种节省内存的开发小技巧。因为当值为整数或双精度浮点数时,由于其本身就是
64
位,就可以不用指针指向了,而是可以直接存在键值对的结构体中,这样就避免了再用一个指针,从而节省了内存空间。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| struct dict {
dictEntry **ht_table[2];
unsigned long ht_used[2];
long rehashidx;
signed char ht_size_exp[2];
int16_t pauseAutoResize;
};
|
- 首先,在正常服务请求阶段,所有的键值对写入哈希表
ht_table[0]
- 接着,当进行 rehash 时,键值对被迁移到哈希表
ht_table[1]
- 最后,当迁移完成后,ht_table[0] 的空间会被释放,并把 ht_table[1]
的地址赋值给 ht_table[0],ht_table[1] 的表大小设置为
0。这样一来,又回到了正常服务请求的阶段,ht_table[0]
接收和服务请求,ht_table[1] 作为下一次 rehash 时的迁移表
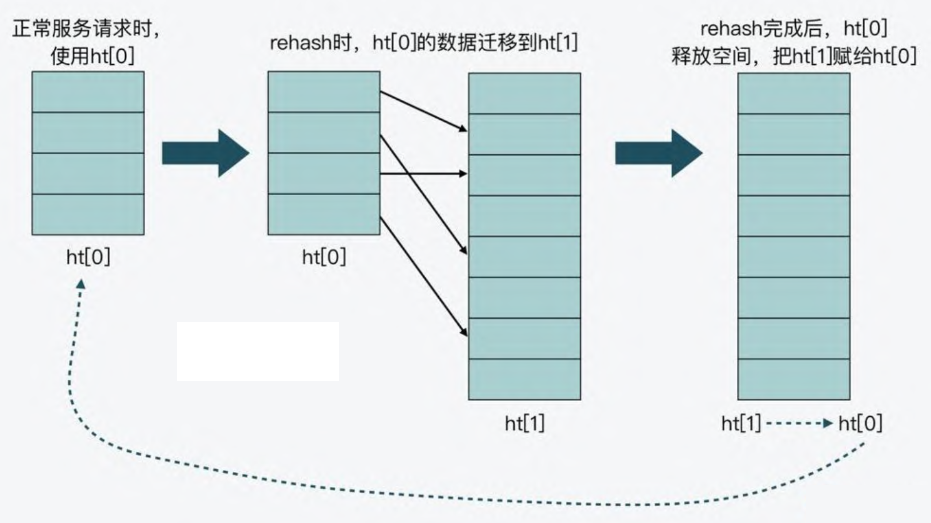 image20250130161526520.png
image20250130161526520.png
rehash
什么时候触发 rehash?
_dictExpandIfNeeded 只有在 dictFindPositionForInsert
中被调用,即插入数据或修改数据的时候。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
static void _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d) {
if (d->pauseAutoResize > 0) return;
dictExpandIfNeeded(d);
}
|
dictExpandIfNeeded 可看出三个可扩容的条件:
- 哈希表 ht_table[0] 大小为 0
- 哈希表允许扩容,并且 ht_table[0] 已有元素大于等于 ht_table[0]
的大小
- 哈希表虽然不允许扩容,但是 ht_table[0] 已有元素 和 ht_table[0]
的大小 比例大于等于
dict_force_resize_ratio(4)就说明哈希表已经严重负载,得扩容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| int dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d) {
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK;
if (DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0]) == 0) {
dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE);
return DICT_OK;
}
if ((dict_can_resize == DICT_RESIZE_ENABLE &&
d->ht_used[0] >= DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0])) ||
(dict_can_resize != DICT_RESIZE_FORBID &&
d->ht_used[0] >= dict_force_resize_ratio * DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0])))
{
if (dictTypeResizeAllowed(d, d->ht_used[0] + 1))
dictExpand(d, d->ht_used[0] + 1);
return DICT_OK;
}
return DICT_ERR;
}
|
dict_can_resize 代表是否开启 rehash。updateDictResizePolicy
会根据实际情况来判断是否需要 rehash。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| void dictSetResizeEnabled(dictResizeEnable enable) {
dict_can_resize = enable;
}
void updateDictResizePolicy(void) {
if (server.in_fork_child != CHILD_TYPE_NONE)
dictSetResizeEnabled(DICT_RESIZE_FORBID);
else if (hasActiveChildProcess())
dictSetResizeEnabled(DICT_RESIZE_AVOID);
else
dictSetResizeEnabled(DICT_RESIZE_ENABLE);
}
|
渐进式 rehash 如何进行?
哈希表在执行 rehash 时,由于 Hash
表空间扩大,原本映射到某一位置的键可能会被映射到一个新的位置上,因此,很多键就需要从原来的位置拷贝到新的位置。而在键拷贝时,由于
Redis 主线程无法执行其他请求,所以键拷贝会阻塞主线程,这样就会产生
rehash 开销。
为了降低 rehash 开销,Redis 就提出了渐进式 rehash 的方法。
渐进式 rehash 的意思就是 Redis
并不会一次性把当前哈希表中的所有键,都拷贝到新位置,而是会分批拷贝,每次的键拷贝只拷贝哈希表中一个
bucket
中的哈希项。这样一来,每次键拷贝的时长有限,对主线程的影响也就有限了。
dictRehash 的核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
int empty_visits = n * 10;
unsigned long s0 = DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0]);
unsigned long s1 = DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[1]);
while (n-- && d->ht_used[0] != 0) {
while (d->ht_table[0][d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
d->rehashidx++;
if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;
}
rehashEntriesInBucketAtIndex(d, d->rehashidx);
d->rehashidx++;
}
return !dictCheckRehashingCompleted(d);
}
|
需要注意的是,一次 rehashing
步骤是将一个桶(可能包含多个键,因为使用了链式存储)。从旧哈希表迁移到新哈希表。然而,由于部分哈希表可能由空桶组成,该函数不能保证每次调用都能
rehash 至少一个桶,因为它最多会访问 N*10
个空桶。这样做是为了避免该函数执行的工作量无法界定,从而可能导致长时间阻塞。
我们不知道哈希表中究竟已经有多少个
桶,通过这种不一次性把所有哈希表中的数据都拷贝来新哈希表中,避免长时间阻塞。
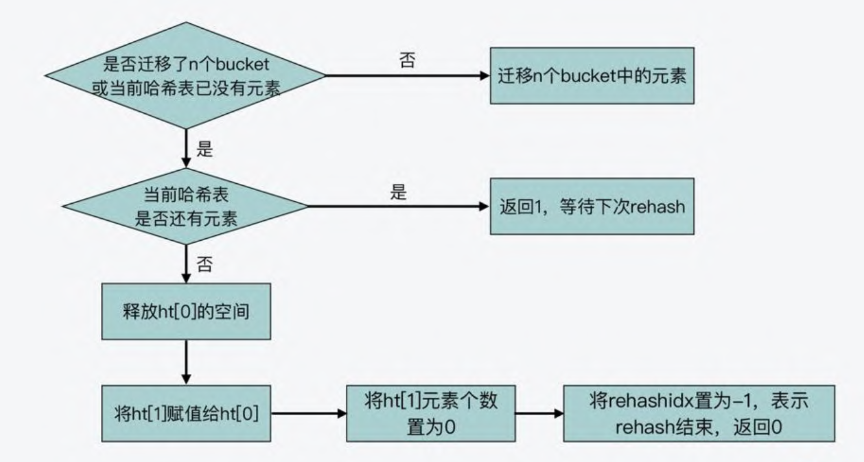 image20250131142103413.png
image20250131142103413.png
dictRehash 会被两个函数调用,即 dictRehashMicroseconds 和
_dictRehashStep。
1
2
3
| static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) {
if (d->pauserehash == 0) dictRehash(d, 1);
}
|
调用情况:
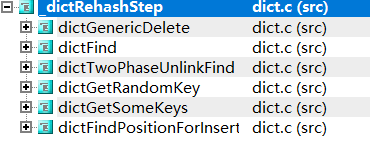 image20250131151318315.png
image20250131151318315.png
_dictRehashStep
函数由字典的常见查找或更新操作调用,使哈希表在被主动使用时 自动从
旧哈希表 迁移到 新哈希表。
下面再看看 dictRehashMicroseconds
函数,会利用空闲时间调用该函数,即在服务器空闲时,利用 CPU
剩余时间逐步完成哈希表数据迁移,减少一次性 rehashing
的性能开销。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| int dictRehashMicroseconds(dict *d, uint64_t us) {
if (d->pauserehash > 0) return 0;
monotime timer;
elapsedStart(&timer);
int rehashes = 0;
while (dictRehash(d, 100)) {
rehashes += 100;
if (elapsedUs(timer) >= us) break;
}
return rehashes;
}
|
CPP 手写哈希表
拉链法
完整代码地址:拉链法解决哈希冲突
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
| #include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
template<typename Key, typename Val>
class HashTableLink {
using HashTable = std::vector<std::list<std::pair<Key, Val>>>;
public:
HashTableLink() : hash_table_(INIT_TABLE_SIZE), elements_(0) {}
void insert(const Key &key, const Val &val) {
if (isRehash()) {
rehash();
}
auto index = hashFun(key);
auto &find_list = hash_table_[index];
for (auto &item : find_list) {
if (item.first == key) {
item.second = val;
return;
}
}
find_list.emplace_back(key, val);
++elements_;
}
bool remove(const Key &key) {
auto index = hashFun(key);
auto &find_list = hash_table_[index];
for (auto it = find_list.begin(); it != find_list.end(); ++it) {
if (it->first == key) {
find_list.erase(it);
--elements_;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool find(const Key &key, Val &val) const {
auto index = hashFun(key);
const auto &find_list = hash_table_[index];
for (const auto &item : find_list) {
if (item.first == key) {
val = item.second;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private:
int hashFun(const Key &key) const {
return std::hash<Key>{}(key) % hash_table_.size();
}
bool isRehash() const {
return (static_cast<double>(elements_) / hash_table_.size()) >= LOAD_FACTOR_THRESHOLD;
}
void rehash() {
auto new_size = hash_table_.size() * 2;
HashTable new_hash_table(new_size);
for (const auto &bucket : hash_table_) {
for (const auto &pair : bucket) {
int newIndex = std::hash<Key>{}(pair.first) % new_size;
new_hash_table[newIndex].emplace_back(pair);
}
}
hash_table_ = std::move(new_hash_table);
}
private:
const int INIT_TABLE_SIZE = 10;
const double LOAD_FACTOR_THRESHOLD = 0.75;
HashTable hash_table_;
size_t elements_;
};
|
容易犯错的地方
rehash:int newIndex = std::hash<Key>{}(pair.first) % new_size
旧哈希表中元素 通过重新计算 哈希,并加入到 新哈希表中。这个过程中
哈希计算不能再用 之前写好的 hashFun,因为 hashFun 中的 hash_table_ 的
size 还没有被更新,得用当前 new_size 参与计算才合理。
线性探测
完整代码地址:线性探测解决哈希冲突
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
| #include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <optional>
template<typename Key, typename Val>
class HashTableArray {
private:
struct Entry {
Key key;
Val value;
bool isActive = false;
Entry(const Key &k, const Val &v) : key(k), value(v), isActive(true) {}
};
using Table = std::vector<std::optional<Entry>>;
public:
HashTableArray() : table_(INIT_TABLE_SIZE), elements_(0) {}
void insert(const Key &key, const Val &val) {
if (isRehashNeeded()) {
rehash();
}
size_t index = findSlot(key);
if (!table_[index].has_value()) {
table_[index] = Entry(key, val);
++elements_;
} else {
table_[index]->value = val;
}
}
bool remove(const Key &key) {
size_t index = findSlot(key);
if (table_[index].has_value() && table_[index]->isActive) {
table_[index]->isActive = false;
--elements_;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool find(const Key &key, Val &val) const {
size_t index = findSlot(key);
if (table_[index].has_value() && table_[index]->isActive) {
val = table_[index]->value;
return true;
}
return false;
}
private:
size_t hashFun(const Key &key) const {
return std::hash<Key>{}(key) % table_.size();
}
size_t findSlot(const Key &key) const {
size_t index = hashFun(key);
while (table_[index].has_value() && table_[index]->key != key) {
index = (index + 1) % table_.size();
}
return index;
}
bool isRehashNeeded() const {
return static_cast<double>(elements_) / table_.size() >= LOAD_FACTOR_THRESHOLD;
}
void rehash() {
size_t new_size = table_.size() * 2;
Table new_table(new_size);
for (auto &entry : table_) {
if (entry.has_value() && entry->isActive) {
size_t index = std::hash<Key>{}(entry->key) % new_size;
while (new_table[index].has_value()) {
index = (index + 1) % new_size;
}
new_table[index] = std::move(entry);
}
}
table_ = std::move(new_table);
}
private:
const size_t INIT_TABLE_SIZE = 10;
const double LOAD_FACTOR_THRESHOLD = 0.75;
Table table_;
size_t elements_;
};
|