第七章:Beast网络库实现WebSocket服务器
接口 Connecting(连接) 处理 WebSocket 流的连接和接收。
(一)连接到 WebSocket 服务器
要与 WebSocket 服务器建立连接,首先需要连接到服务器,然后执行
WebSocket 握手。Boost.Beast 提供了一个 stream 类来管理
WebSocket 连接。你可以使用 tcp_stream
作为底层流来实现这一点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <boost/asio.hpp> #include <boost/beast.hpp> #include <iostream> namespace net = boost::asio;namespace beast = boost::beast;using tcp = net::ip::tcp;int main () try {websocket::stream<tcp::socket> ws (ioc) ;tcp::resolver resolver (ioc) ;auto const results = resolver.resolve ("example.com" , "ws" );get_lowest_layer (ws).connect (results);handshake ("example.com" , "/" );"Connected and handshake completed" << std::endl;catch (std::exception const & e) {"Exception: " << e.what () << std::endl;
(二)接收来自客户端的连接
要接受传入的 WebSocket 连接,你需要创建一个 acceptor
对象来监听连接请求。接受到连接后,你可以创建一个 stream
对象来处理 WebSocket 连接。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <boost/asio.hpp> #include <boost/beast.hpp> #include <iostream> namespace net = boost::asio;namespace beast = boost::beast;using tcp = net::ip::tcp;int main () try {tcp::acceptor acceptor (ioc, tcp::endpoint(tcp::v4(), 0 )) ;listen ();"Listening for connections on port " << acceptor.local_endpoint ().port () << std::endl;tcp::socket socket (ioc) ;accept (socket);websocket::stream<tcp::socket> ws (std::move(socket)) ;accept ();"Connection accepted and handshake completed" << std::endl;catch (std::exception const & e) {"Exception: " << e.what () << std::endl;
(三)使用 acceptor 直接接收连接到 WebSocket 流
如果你希望 WebSocket 流在接受连接时直接使用
acceptor,可以这样做:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <boost/asio.hpp> #include <boost/beast.hpp> #include <iostream> namespace net = boost::asio;namespace beast = boost::beast;using tcp = net::ip::tcp;int main () try {tcp::acceptor acceptor (ioc, tcp::endpoint(tcp::v4(), 0 )) ;listen ();websocket::stream<tcp::socket> ws (net::make_strand(ioc)) ;accept (beast::get_lowest_layer (ws).socket ());accept ();"Connection accepted and handshake completed" << std::endl;catch (std::exception const & e) {"Exception: " << e.what () << std::endl;
Handshaking(握手) (一)客户端
WebSocket 会话开始于客户端发送一个 HTTP/1.1
升级请求,通过建立的连接请求 WebSocket
协议。服务器收到请求后,发送一个表示接受请求并将连接升级的响应。这个升级请求必须包含
Host 字段和请求的目标资源。下面是一个典型的 HTTP
升级请求的示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 GET / HTTP/1.1 2 pGeTR0DsE4dfZs2pH+8 MA==13 216
使用 websocket::stream 类的 handshake 和
async_handshake 成员函数可以发送带有所需 Host
和目标字符串的请求。下面的代码展示了如何在客户端角色中连接到服务器,并执行
WebSocket 握手:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <boost/asio.hpp> #include <boost/beast.hpp> #include <iostream> namespace net = boost::asio;namespace beast = boost::beast;using tcp = net::ip::tcp;int main () try {websocket::stream<tcp::socket> ws (ioc) ;tcp::resolver resolver (ioc) ;get_lowest_layer (ws).connect (resolver.resolve ("www.example.com" , "ws" ));handshake ("www.example.com" , "/" );"Connected and handshake completed" << std::endl;catch (std::exception const & e) {"Exception: " << e.what () << std::endl;
在客户端收到 HTTP 升级响应后,可能希望对收到的 HTTP
响应消息执行额外的验证。例如,检查基本认证挑战的响应是否有效。可以通过重载的
handshake 成员函数,将收到的 HTTP 消息存储到
response_type 类型的输出引用参数中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 #include <boost/asio.hpp> #include <boost/beast.hpp> #include <iostream> namespace net = boost::asio;namespace beast = boost::beast;using tcp = net::ip::tcp;int main () try {websocket::stream<tcp::socket> ws (ioc) ;tcp::resolver resolver (ioc) ;get_lowest_layer (ws).connect (resolver.resolve ("www.example.com" , "ws" ));handshake (res, "www.example.com" , "/" );"Connected and handshake completed with response" << std::endl;catch (std::exception const & e) {"Exception: " << e.what () << std::endl;
(二)服务端
使用 accept 和 async_accept
成员函数可以读取 WebSocket HTTP 升级请求握手,并发送 WebSocket HTTP
升级响应:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <boost/asio.hpp> #include <boost/beast.hpp> #include <iostream> namespace net = boost::asio;namespace beast = boost::beast;using tcp = net::ip::tcp;int main () try {tcp::acceptor acceptor (ioc, tcp::endpoint(tcp::v4(), 0 )) ;listen ();tcp::socket socket (ioc) ;accept (socket);websocket::stream<tcp::socket> ws (std::move(socket)) ;accept ();"Connection accepted and handshake completed" << std::endl;catch (std::exception const & e) {"Exception: " << e.what () << std::endl;
(三)握手缓冲
服务器可以从流中读取数据,并在后续决定这些缓冲的字节是否应该解释为
WebSocket 升级请求。为此,提供了接受额外缓冲序列参数的
accept 和 async_accept 重载函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <boost/asio.hpp> #include <boost/beast.hpp> #include <string> namespace net = boost::asio;namespace beast = boost::beast;using tcp = net::ip::tcp;int main () try {tcp::acceptor acceptor (ioc, tcp::endpoint(tcp::v4(), 0 )) ;listen ();tcp::socket socket (ioc) ;accept (socket);websocket::stream<tcp::socket> ws (std::move(socket)) ;read_until (ws, net::dynamic_buffer (s), "\r\n\r\n" );accept (net::buffer (s));"Connection accepted and handshake completed with buffered data" << std::endl;catch (std::exception const & e) {"Exception: " << e.what () << std::endl;
(四)检查 HTTP 请求
当实现一个支持 WebSocket 的 HTTP
服务器时,服务器通常会读取来自客户端的 HTTP 请求。可以使用
websocket::is_upgrade 函数来检测传入的 HTTP 请求是否为
WebSocket 升级请求。
如果 HTTP 请求是 WebSocket 升级请求,可以使用重载的
accept 和 async_accept 函数,这些函数接受整个
HTTP 请求头作为对象,以执行握手。通过手动读取请求,可以处理普通的 HTTP
请求以及升级请求。示例如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 #include <boost/asio.hpp> #include <boost/beast.hpp> #include <iostream> namespace net = boost::asio;namespace beast = boost::beast;using tcp = net::ip::tcp;int main () try {tcp::acceptor acceptor (ioc, tcp::endpoint(tcp::v4(), 0 )) ;listen ();tcp::socket socket (ioc) ;accept (socket);read (socket, buffer, req);if (beast::websocket::is_upgrade (req)) {websocket::stream<tcp::socket> ws (std::move(socket)) ;BOOST_ASSERT (buffer.size () == 0 );accept (req);"WebSocket upgrade request accepted" << std::endl;else {"Normal HTTP request received" << std::endl;catch (std::exception const & e) {"Exception: " << e.what () << std::endl;
(五)子协议
如果客户端请求一组子协议中的一个,客户端将在初始 WebSocket 升级 HTTP
请求中设置 Sec-WebSocket-Protocol
头。服务器需要解析该头并选择一个接受的协议。服务器通过在接受头中设置
Sec-WebSocket-Protocol 头来指示选定的协议。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 #include <boost/asio.hpp> #include <boost/beast.hpp> #include <array> #include <algorithm> #include <string> namespace net = boost::asio;namespace beast = boost::beast;using tcp = net::ip::tcp;auto select_protocol = [](beast::string_view offered_tokens) -> std::string {offered (offered_tokens);static const std::array<beast::string_view, 3> supported = {{"v3.my.chat" ,"v2.my.chat" ,"v1.my.chat" for (auto proto : supported) {auto iter = std::find (offered.begin (), offered.end (), proto);if (iter != offered.end ()) {assign (proto.begin (), proto.end ());break ;return result;int main () try {tcp::acceptor acceptor (ioc, tcp::endpoint(tcp::v4(), 0 )) ;listen ();tcp::socket socket (ioc) ;accept (socket);read (socket, buffer, req);if (beast::websocket::is_upgrade (req)) {select_protocol (req[beast::http::field::sec_websocket_protocol]);if (protocol.empty ()) {result (beast::http::status::bad_request);body () = "No valid sub-protocol was offered. This server implements v3.my.chat, v2.my.chat, and v1.my.chat" ;write (socket, res);else {ws (std::move (socket));set_option (beast::websocket::stream_base::decorator (set (beast::http::field::sec_websocket_protocol, protocol);accept (req);"WebSocket upgrade request accepted with selected protocol: " << protocol << std::endl;else {"Normal HTTP request received" << std::endl;catch (std::exception const & e) {"Exception: " << e.what () << std::endl;
Decorator(装饰器) 使用 Boost.Beast 提供的装饰器(decorator)功能来修改 WebSocket 的
HTTP 升级请求和响应。装饰器允许程序在发送 HTTP
消息之前修改这些消息,从而实现自定义的 HTTP 头字段或其他行为。
装饰器 :可以是函数指针或可调用对象,在 WebSocket
实现发送 HTTP 消息之前被调用。
装饰对象类型 :
request_type:代表 HTTP 升级请求的类型。response_type:代表 HTTP 升级响应的类型。stream_base::decorator:用于持有装饰器对象,通过
set_option 方法应用到流上。
可以通过 set_option 将装饰器设置到 stream
对象上。装饰器必须在握手(handshake)或接受连接(accept)之前设置。以下是几个典型的使用方式:
(一)普通函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 void set_user_agent (request_type& req) set (http::field::user_agent, "My User Agent" );stream<tcp_stream> ws (ioc) ;set_option (stream_base::decorator (&set_user_agent));
(二)函数对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 struct set_server void operator () (response_type& res) {set (http::field::user_agent, "My Server" );set_option (stream_base::decorator (set_server{}));
(三)Lambda 表达式
1 2 3 4 5 ws.set_option (stream_base::decorator (set (http::field::user_agent, "My Server" );
(四)同时处理请求和响应
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 struct set_message_fields void operator () (request_type& req) {set (http::field::user_agent, "My User Agent" );void operator () (response_type& res) {set (http::field::user_agent, "My Server" );set_option (stream_base::decorator (set_message_fields{}));
装饰器对象通过 衰退复制(decay-copy) 转移到
stream,因此支持移动类型。可以使用
std::unique_ptr 等资源管理对象:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 struct set_auth void operator () (request_type& req) {set (http::field::authorization, *key);set_option (stream_base::decorator (make_unique <std::string>("Basic QWxhZGRpbjpPcGVuU2VzYW1l" )}));
注意:装饰器不应 修改 WebSocket 升级特定的字段(如
Upgrade 或 Connection
字段),否则会导致未定义行为。
Message 消息可以是文本(UTF-8 编码)或二进制。文本消息必须是有效的 UTF-8
字符串,这在接收时会进行验证,但在发送时不会检查。
(一)发送消息
发送完整消息 :可以使用 write 或
async_write 函数一次性发送完整的消息。
发送部分消息 :可以通过 write_some 或
async_write_some
函数分段发送消息,适用于将消息分割为多个帧的情况。
1 2 3 net::const_buffer b ("Hello, world!" , 13 ) ;text (true ); write (b);
(二)接收消息
读取完整消息 :可以使用 read 或
async_read 函数将完整消息读取到动态缓冲区中。
读取部分消息 :如果消息较大或者需要逐步处理,可以使用
read_some 或 async_read_some
函数分段读取。这适用于流媒体或处理无法一次加载到内存中的大型数据。
1 2 3 4 5 flat_buffer buffer;read (buffer);text (ws.got_text ());write (buffer.data ());consume (buffer.size ());
注:websocket::stream 类是
非线程安全的 ,因此其成员函数的调用必须在同一
strand(线程或任务序列)中进行,以避免竞争条件。
Timeouts 与基础的 tcp_stream 或 basic_stream
的通用超时机制不同,WebSocket 流提供了一套更复杂的超时配置,专门用于
WebSocket 通信。
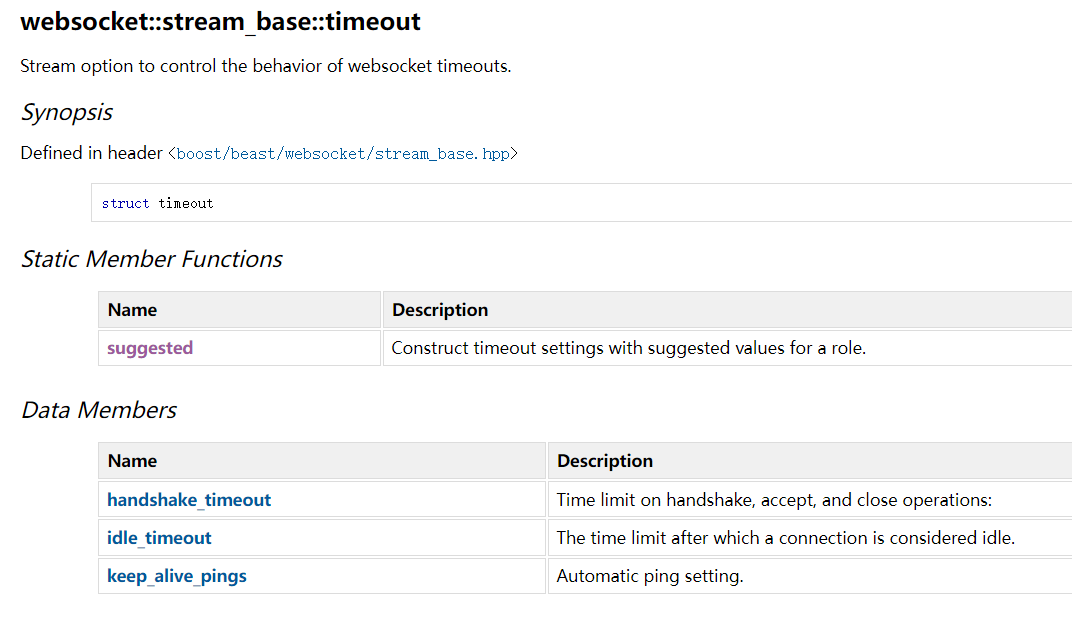
stream_base::timeout :表示 WebSocket
流的超时设置。
timeout.png
stream_base::timeout::suggested :根据角色(客户端或服务端)返回建议的超时设置。
stream::set_option :用于将超时和其他设置应用到
WebSocket 流上。
(一)设置建议的超时
1 2 set_option (stream_base::timeout::suggested (role_type::server));
(二)手动设置超时
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 stream_base::timeout opt{seconds (30 ), none (), false set_option (opt);
(三)超时通知
当超时发生时,系统会关闭套接字或流,并通过 async_read
的完成处理器传递超时错误(error::timeout)。
不需要手动关闭连接,系统会自动关闭。
1 2 3 4 5 6 ws.async_read (b,size_t )if (ec == beast::error::timeout)"timeout, connection closed!" ;
重要注意事项
WebSocket 的超时功能仅在异步 I/O 操作时可用。
WebSocket 流的超时机制与 tcp_stream
的超时机制不兼容 。如果从一个启用了超时的
tcp_stream 构造 WebSocket 流,应首先禁用
tcp_stream 的超时
1 2 3 4 5 expires_never ();stream<tcp_stream> ws (std::move(sock)) ;
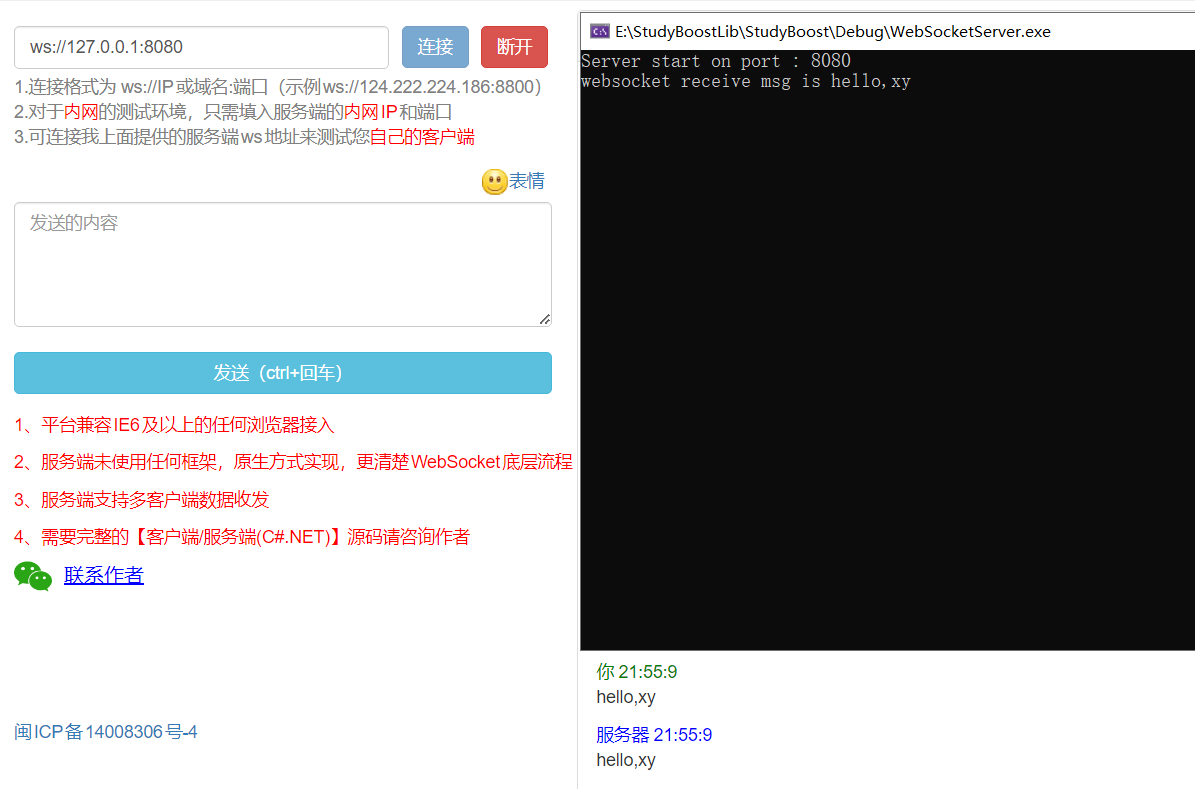
代码实现和测试 在输入框中输入
ws:://127.0.0.1:8080,点击连接,网站会提示连接成功。然后到输入框中输入你要发送的数据,服务器接收到之后会回复相同的信息。
websocket.png
测试网址:http://websocket-test.com/
代码地址:实现WebSocketServer
⭐️内容取自 B 站 UP 恋恋风辰和 mmoaay 的《Boost.Asio C++
网络编程》,仅从中取出个人以为需要纪录的内容。不追求内容的完整性,却也不会丢失所记内容的逻辑性。如果需要了解细致,建议看原视频或者读原书。